

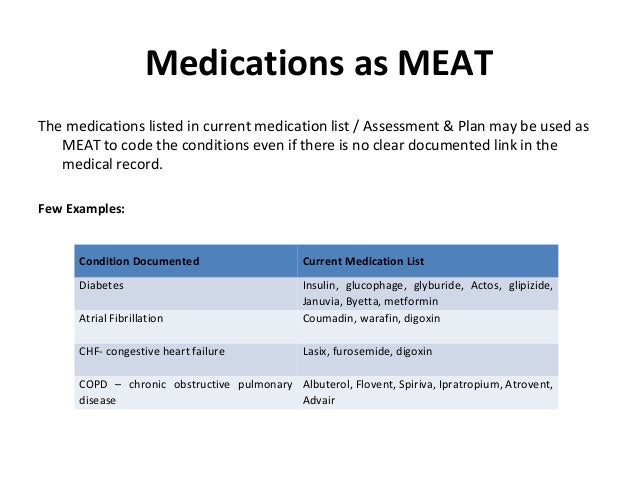
M-Monitor signs and symptoms (disease process)Į-Evaluate (test results, meds, patient response to treatment)Ī-Assess (ordering tests, patient education, review records, counseling patient and family) MEAT is an acronym used in HCC coding to ensure the most accurate information is being documented for a patient: For HCC coding to be successful, the doctor can accomplish documentation standards by using MEAT. A provider must report on each patient’s risk adjustment diagnosis and it must be based on clinical documentation from a face-to-face encounter. Specificity is key when it comes to HCC coding and documentation. The specific HCC category to which a diagnosis is assigned determines its contribution to the RAF calculation. Each of the 86 categories is then placed into a hierarchy of risk. Out of 72,616 ICD-10-CM codes CMS identified 9,700 diagnosis associated with higher-than-average costs and then assigned them into 86 disease categories. HCCs are diseases or conditions organized into body systems or comparable disease processes that Medicare correlated with increased cost of care. So, what are HCC’s? Medicare uses HCCs to reimburse Medicare Advantage plans based on their current member’s health. A patients RAF score is heavily weighted on HCC’s. A multitude of factors determine the amount of risk and work involved to maintain the health of a patient. The risk assessment data used is based off claims and medical records collected from doctors’ offices, in-patient hospital visits and outpatient clinics. Within this payment model, patients in the same practice could have a different payment rate. This score measures how costly a patient is predicted to be for the current year. Risk Adjustment Factor or RAF uses a patient’s demographics and diagnosis to determine that patients risk score. To better understand HCC coding, lets first break down Risk Adjustment Factor. As healthcare shifts towards more value-based payment models HCC coding is becoming more prevalent of a topic. It was only implemented in 2004 and was designed to identify patients with serious or chronic illness and assign a risk factor score to the person based upon a combination of a patient’s health conditions and demographic details. Risk Adjustment and Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding is a payment model mandated by CMS in 1997, originally created to estimate future costs for a patient. Risk adjustment and HCC coding is a major contributor to communicating the true complexity of a patient cohort. Cost/utilization is greatly impacted by a patient’s annual complexity account, but providers are only paid when the payers understand their patient’s true complexity.

An additional component of payment is based on the complexity of the patient population for which each provider provides healthcare services.
Value-based healthcare is a healthcare delivery model where healthcare providers are paid based on patient health outcomes instead of based on the volume of patients seen and services delivered.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
